polarimeter enantiomeric excess|enantiomeric excess examples : member club The sample consists of 75 % of the racemic form (=equimolar mixture of both enantiomers, α=0 o) and an excess of 25 % of the enantiomer in question (62.5 % and 37.5 %). The instrument used below allows you to calculate the .
web26 de abr. de 2023 · 主題(トピック)を表すときは「は」を使う. 否定したい部分をはっきり言いたいときは「は」を使う. 対比するときは「は」を使う. 目や耳に入ってくること、気づいたこと(発見)を言うときは「が .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 19 de fev. de 2019 · 1º Habilite o uso de filtros clicando no botão Usar Filtros, 2º Desça e procure pelo botão Exibir Filtros de Linhas , clique nele para visualizar todos os filtros sobre linhas. Para utilizar basta marcar qualquer filtro que ele já ficará ativo na geração das apostas, caso queria pode .
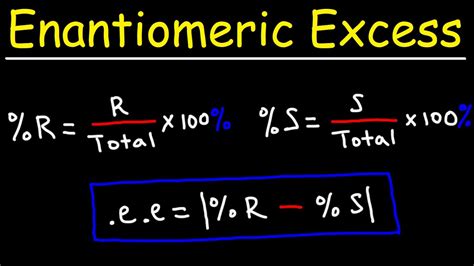
When a mixture contains more of one enantiomer than the other, chemists often use the concept of enantiomeric excess (ee) to quantify the difference. Enantiomeric excess can be expressed as: \[e e=\frac{(\% \text { more abundant enantiomer }-50) \times 100\%}{50} \nonumber \] The rotation angles can be measured by using polarimeter (later in this section). For a pair of enantiomers with same concentration, under the same condition, they rotate the plane of polarization with the same angles but . When a mixture contains more of one enantiomer than the other, chemists often use the concept of enantiomeric excess (ee) to quantify the difference. Enantiomeric .
gas analyzers def
Thus, the optical purity is thus equal to the percentage excess of the major enantiomer over the minor enantiomer. This term, the .When a beam of ordinary light is passed through a polarizing lens, light waves that oscillate in only a single plane are obtained. This light is said to be plane polarized. Rotation of plane .
The sample consists of 75 % of the racemic form (=equimolar mixture of both enantiomers, α=0 o) and an excess of 25 % of the enantiomer in question (62.5 % and 37.5 %). The instrument used below allows you to calculate the .The enantiomeric excess (ee) tells how much of an excess of one enantiomer is in the mixture, and it can be calculated as: We will use a series of hypothetical examples in the next table for a detailed explanation.A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. . Enantiomeric Excess. The "optical purity" is a comparison of the optical rotation of a pure sample of unknown .
There are a couple different ways to calculate enantiomeric excess. If you have the specific concentration of each, ee% = 100 x (maj. enantiomer conc. - min. enantiomer conc.)/(maj. enantiomer .If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Enantiomeric excess is crucial for understanding optical activity. Specific rotation indicates the degree of rotation caused by pure enantiomers. A racemic mixture (50% S and 50% R) results in zero optical activity due to cancellation. . Using a 1.0-cm polarimeter cell and a solution prepared by dissolving 2.54 g of glucose in 1 L of H₂O .frequently asked questions What is enantiomeric excess and how is it calculated in stereochemistry? Enantiomeric excess is a measure of the excess of one enantiomer over the other in a mixture. In stereochemistry, it is calculated by subtracting the percentage of one enantiomer from 50%, with the result representing the excess of the other enantiomer. The (-)-X is in excess. The mixture contains 67 % (-)-X and 33 % (+)-X. > The rotations of the two enantiomers cancel each other, so the rotation of the mixture will be that of the excess enantiomer. The mixture has a negative sign of rotation, so (-)-X is in excess. To calculate the enantiomeric excess, you divide the observed specific rotation by the maximum . An undergraduate chemistry experiment that draws from primary research is described. The experiment exploits chiral supramolecular assemblies for the determination of enantiomeric excess by 1H NMR spectroscopy. This report describes the delivery of the experiment to a cohort of students, and as a result of feedback from those involved, an .
Polarimeter Light Sources. It is now common practice to use other light sources such as xenon or tungsten halogen. With appropriate filters, these light sources offer advantages of cost, long life, and broad wavelength emission range over traditional light sources. . known as enantiomeric excess. Let’s say a chemist was attempting to .Select one or more: Measured rotation of light Density of the sample Pathlength of the sample container O Enantiomeric excess of the sample . Show transcribed image text. There are 2 steps to solve this one. . What parameters are included in the specific rotation calculation of a pure substance based on measurement from a polarimeter? Select .
Abstract Enantiomeric excess (ee) is an essential indicator of chiral drug purification in the pharmaceutical industry. . chiroptical response of the present approach is ≈30-fold higher than that of the conventional optical rotation-based polarimeter, and the reagent consumption is reduced by three orders of magnitude. 1 Introduction .
Enantiomeric Excess. The "optical purity" is a comparison of the optical rotation of a pure sample of unknown stereochemistry versus the optical rotation of a sample of pure enantiomer. It is expressed as a percentage. If the sample only rotates plane-polarized light half as much as expected, the optical purity is 50%.In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. . α=0 o) and an excess of 25 % of the enantiomer in question (62.5 % and 37.5 %). The instrument used below allows you to calculate the specific rotation, if you know the .You are tasked with finding the enantiomeric excess of a sample of R-carvone. You dissolve 1.429 g of the liquid in ethanol and dilute to exactly 9.0 mL. You put this liquid in a polarimetry cell that measures 10 cm in length. When you read the sample in a polarimeter, you find a rotation of .
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. .Enantiomeric excess (ee) is a valuable measurement in the world of stereochemistry, as it quantifies the purity of a chiral mixture in terms of its enantiomers. . varying ratios of enantiomers can contribute to different optical activities when using a polarimeter. The term enantiomeric excess helps us understand how much excess of one .12. A pure sample of the Senantiomer of a compound has specific rotation, [a], of +100°. A solution containing 0.20 g/mL of a mixture of enantiomers rotates plane polarized light by -16° in a 1 dm polarimeter. What is the enantiomeric .
A pure sample of the R enantiomer of a compound has a specific rotation, ( a), of +20 °. A solution containing 0.2 g/mL of a mixture of enantiomers rotates plane polarized light by -2 ° in a I dm polarimeter. What is the enantiomeric excess (%ee) of .Question: The specific rotation of Compound X is +160.5o . A mixture of Compound X and its enantiomer are placed in the polarimeter and the observed rotation is +60.1o . Which enantiomer is in excess? (+ or -) Calculate the enantiomeric excess. Show your work. Calculate the percentage of each enantiomer in the mixture.The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. . The enantiomeric excess (ee) tells how much of an excess of one enantiomer is in the mixture, and it can be calculated as:
This organic chemistry video explains how to calculate enantiomeric excess given the grams of the R and S stereoisomers.Full 7 Hour Organic Chemistry Exam 2 .
To sketch the approximate mixture of enantiomers in a polarimeter tube, first calculate the percentages of each enantiomer using the enantiomeric excess (ee) and the relevant equations. Once you have the percentages, represent the mixture visually by dividing the tube into sections proportional to these percentages.The specific rotation of Compound X is +160.5o. A mixture of Compound X and its enantiomer are placed in the polarimeter and the observed rotation is +60.1o. Which enantiomer is in excess? (+ or -) Calculate the enantiomeric excess. Show your work. Calculate the percentage of each enantiomer in the mixture.
Question: 11. A pure sample of the R enantiomer of a compound has a specific rotation of -15°. A solution containing 0.6 g/mL mixture of enantiomers rotates plane polarized light by -3° in a 1 dm polarimeter. What is the enantiomeric excess of the mixture? a. 33% R b. 33% S c. 50%R d. 75%S 12. Which of the following represents a cis isomer?A solution containing 0.2 g/mL of a mixture of enantiomers rotates plane polarized light by −2° in a 1 dm polarimeter. What is the enantiomeric excess (%ee) of the mixture? a.25% R. b.40% S. c.50% S. d.70% R. Like. 0. All replies. Answer. 10 months ago. The correct answer is option c.A student makes up a 45 g : 25 g (S:R respectively) mixture of the enantiomers of ephedrine and places it in a polarimeter. The cell length of the polarimeter is 1.00 dm and the concentration of the sample is 0.50 g/ml. Calculate the observed rotation and the .The chiral purity of compounds is characterized by the enantiomeric excess (ee) or the diastereomeric excess (de). Enantiomeric excess (synonyms are enantiomer excess or enantiomeric purity) is defined as the proportion of one enantiomer in a given mixture of both enantiomers [29]:
how to quantify enantiomeric excess
web22/04/2022 16h06 Atualizado há um ano. Hadson Nery deixou o Peixe da Amazônia por motivos pessoais — Foto: Reprodução/Rede Amazõnica. Durou 20 dias a estadia do ex .
polarimeter enantiomeric excess|enantiomeric excess examples